VFD DRIVES TROUBLESHOOTING
In this article, we discuss Common Faults and Solutions of Variable Frequency Drives (VFD Drives Troubleshooting Common Fault Codes).
Welcome to the Insight Control System Blog Page.
Basic Working
Principle:
- AC Power Input: The VFD draws AC power from the grid (usually three-phase, but there are single-phase models). A rectifier converts this electricity to direct current (DC).
- DC Bus: The DC power is then stored in the DC bus, which is built into the VFD's internal circuitry.
- Inverter: An inverter converts DC electricity back to AC power. The inverter uses semiconductor switches (such as IGBTs) to change the frequency of the AC power, which regulates the motor speed.
- By altering the output frequency, the VFD directly regulates the motor's speed, allowing for a wide range of applications requiring precision motor control.
How
VFDs Control Motor Speed:
Frequency Control:
- An AC motor's speed is directly proportional to the frequency of the electricity supplied to it.
- The VFD's frequency output can be adjusted to vary the motor's speed.
- For example, doubling the power's frequency (Hz) doubles the motor's speed.
Voltage Control:
- VFDs also change the voltage supplied to the motor in relation to its frequency, ensuring that it operates smoothly and effectively.
- This maintains a consistent voltage-to-frequency ratio, also known as the V/f control.
Basically, check for the following faults during operation.
- Motor operation fault,
- Improper installation environment,
- Cooling system fault,
- Abnormal vibration, abnormal noise,
- Abnormal overheat, discoloration,
1.Drive does not start
Causes:
- Drive not ready,
- Drive not receiving a Run Signal,
- Active fault,
- DC bus too high or low,
- Run enable input not present,
Control place not correct Example trying to start from I/O
when active control place is keypad.
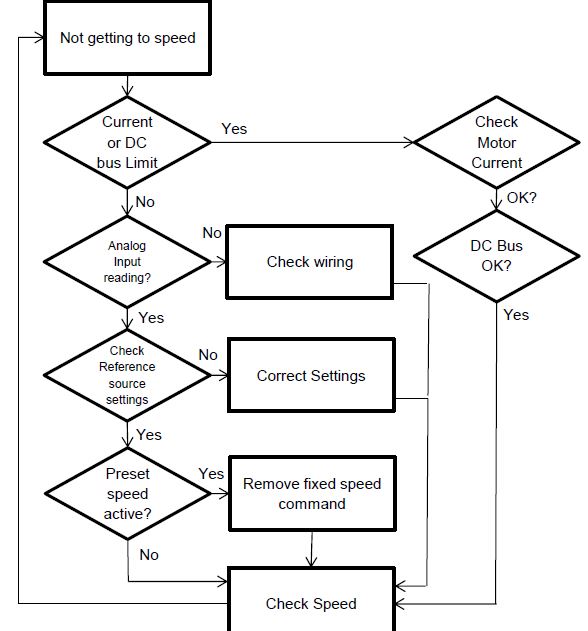
2.Drive does not get to speed
Causes:
- Missing reference,
- Preset speed or jog speed active,
Missing Reference:
- Check analog input monitor,
- Check that the drive is programmed to follow the correct input,
- Ensure the drive is not hitting any other limits,
- Check frequency reference compared to output frequency,
3.Overcurrent
Causes:
- Incorrect motor parameters,
- Mechanical fault,
- Electrical fault,
- Current measurement error,
Solution:
- Check wiring and motor for insulation failures and proper connections.
- Check for mechanical overload, Locked rotor.
- Check for proper drive size.
4.Current Limit Controller
Causes:
- Incorrect motor parameters,
- Mechanical fault,
- Electrical fault,
- Current measurement error,
Solution:
- Not all models have an indication when the current limit is reached.
- Current limit will reduce output frequency to reduce output current to at or below the current limit setting.
5.Ground Fault
Causes:
- Faulty motor,
- Electrical fault,
- Current measurement error,
- Check for loose or high resistance connections to the motor.
- Test motor for electrical failure.
- Disconnect motor leads or apply known good motor to verify current measurements.
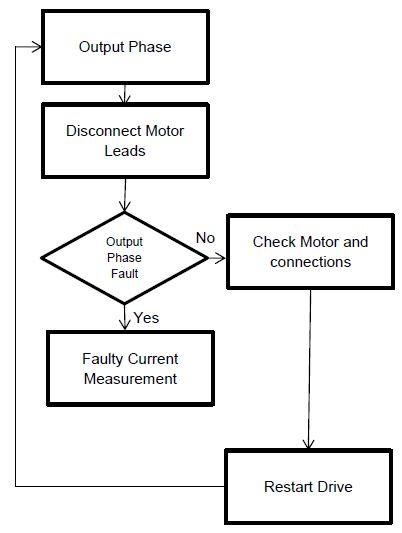
6.Output Phase Fault
Causes:
- Loose Motor Connections,
- Faulty Motor,
- Current measurement error,
- Caused by current imbalance on the output of the VFD.
- Look for loose connections or fault in motor winding's.
7.Overvoltage Fault
Causes:
- High Line Voltage,
- Regenerated voltage from load,
- Excessive line side harmonics,
- If Fault occurs during deceleration or stop command, then increase deceleration time or brake chopper may be needed.
- Cyclic loads may need regen unit or brake chopper.
- Excess harmonics may be overcharging DC link capacitors.
8.Overvoltage Controller
Causes:
- High Line Voltage,
- Regenerated voltage from load,
- Excessive line side harmonics,
- Trouble shooting is the same as for the overvoltage fault, the overvoltage controller will increase the reference in an attempt to bleed off excess voltage.
- Not all series of VFD’s have an indication of when this controller is active.
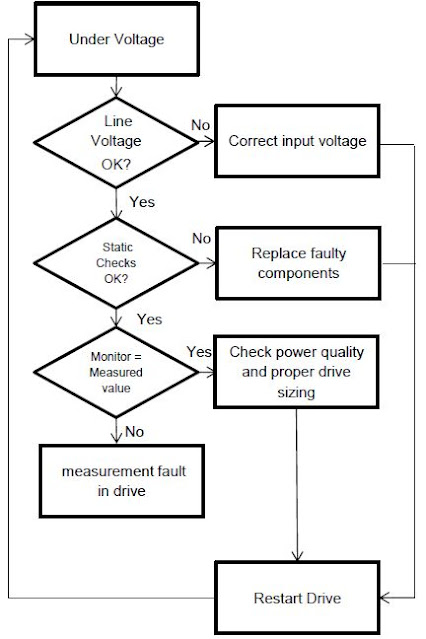
9.Undervoltage Fault
Causes:
- Low Line Voltage,
- Improperly sized drive,
Solution:
- Check for low line voltage or drops in line voltage under load.
- Check for damaged input rectifiers with static checks.
- Check for even current draw on input when drive is running.
10.Unit Over Temperature
Causes:
- High Ambient temperature,
- Insufficient airflow,
- Plugged heat sink,
- Failed cooling fan,
Solution:
- Check Main cooling fan for rotation.
- Ensure unobstructed heat sink and airflow.
- Check ambient temperature is below the drives ratings.
11.Motor Over Temperature
- Overloaded Motor,
- Operating Motor at high load at low speeds,
- Undersized Motor,
- Incorrect Motor Parameters,
- Check Motor Parameters.
- Observe current and speed.
- Current should be nearly proportional to speed, if running half speed at FLA drive will protect motor from increased thermal stress from reduced cooling.
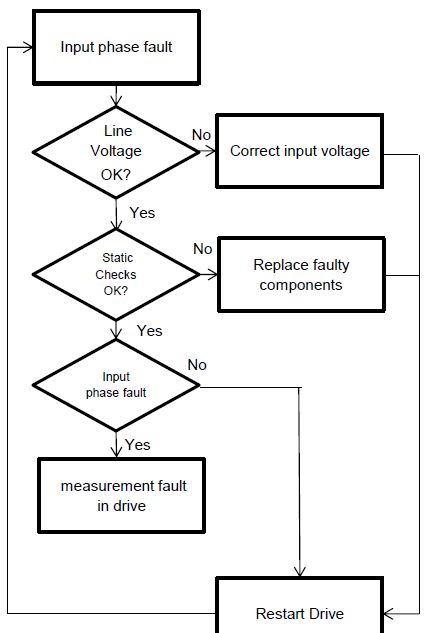
12.Input Phase Fault
Causes:
- Missing Input phase,
- Damaged Drive,
Solution:
- Check for Line Voltage imbalance.
- Check for loose connections or blown fuses.
- Check for damaged input rectifiers with static checks.
- Single phase input drives need to have this protection disabled.
- Check for even current draw on input when drive is running.
- These are the Fault causes and solutions for variable frequency drives.
🔗 Connect with Me:
╰┈➤YouTube
╰┈➤Tumblr
╰┈➤Slide share
╰┈➤Quora
I hope you learnt something from this article📖
Please provide feedback on this article; this will help me improve my feature Blog Post. 📝
Come look around, leave a comment, and contact us; I always like hearing from you.
Have a wonderful day.❤️
Thank you for visiting🙏









Useful
ReplyDelete